
Mata Ortiz and Casas Grandes
$ 8000
xxcgg8120
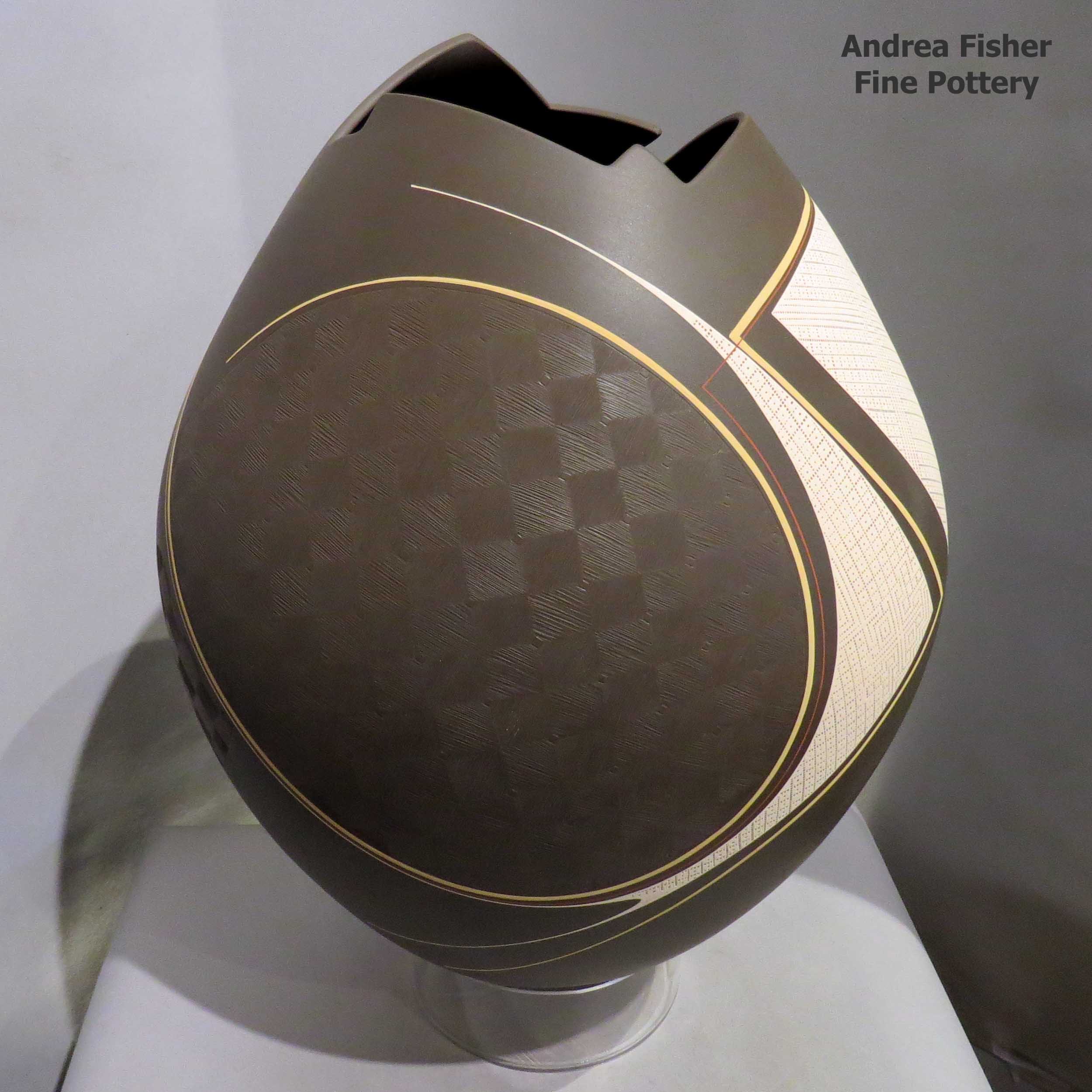
Polychrome jar with geometric opening and sgraffito texture and painted geometric design
15.75 in H by 11.5 in Dia
Condition: Excellent
Signature: Diego Valles
Date Created: 2018
Tell me more! Buy this piece!
(505) 986-1234 - www.andreafisherpottery.com - All Rights Reserved
Diego Valles
Mata Ortiz and
Casas Grandes


Diego Gerardo Valles Trevizo learned the full range of Mata Ortiz shapes and styles, then struck out on his own in the direction of pure contemporary shapes decorated with stylized ancient designs. Some of his vessels are skeletonized, some undecorated, some with finely painted patterns that run parallel to the rims of his cutouts. His vision and the embodiment of that vision in his pieces is credited with expanding the boundaries of Mexican ceramics.
Diego came into this world in July, 1982 as the son of Diego Valles (deceased) and Angeles Trevizo. He says he made his first pot when he was about 8 years old and he's been hooked ever since. He counts Antonia Tena and Jesus Mora as his primary teachers. Despite becoming an electromechanical engineer, Diego is most proud of his accomplishments in ceramics, especially when he won the 2010 National Youth Award for Arts. He says accepting that award in person from then-Presidente Felipe Calderon was one of the proudest moments in his life.
Over the last couple decades Diego has traveled the world giving demonstrations and offering workshops about how he makes his pots. His works are shown in some of the finest ceramics museums in the world, like the American Museum of Ceramic Art in Pomona, CA, and the Nerman Museum of Contemporary Art in Overland Park, KS. He also participated in the first show organized by the Museo de Arte Indigena Contemporaneo (MAIC), managed by Espacias de Arte Nomada AC. That was a traveling exhibition that began in Montreal, PQ, Canada, then moved to Boston, New York, Washington, Austin, Ciudad Obregon, the Cabos, Riviera Maya and Mexico City.
Diego tells us his favorite shapes to work with are sculptural vases and his favorite designs tend to be in red and/or black. He says he draws his inspiration from the nature around Mata Ortiz and the culture of Paquimé. He also wants the world to know he believes in God.
Diego is married to fellow potter/engineer Carla Martinez and they have two beautiful daughters.
Among his other accomplishments:
- The Juan Quezada Celado Excellence Award at the 2023 Concurso Anual de la Ceramica de Mata Ortiz
- First ceramic artist to be Artist-in-Residence at Taliesin West, the Frank Lloyd Wright School of Architecture, Fall 2012
- People's Choice Award at the 2012 4th Biennial Concordia Continental Ceramics
- Proposed by the National Youth Institute as a candidate for the 2011 National Arts and Sciences Award
- First Prize at the Concurso Municipal de Cerámica in September 2011
- Best of Show at the 2010 3rd Biennial Concordia Continental Ceramics
- Best of Show at the 2009 Concurso Anual de la Cerámica de Mata Ortiz
- Best of Show at the 2008 Binational Painting Competition at the Museo de las Culturas del Norte y Zona Arqueológica de Paquimé
- First Prize at the 2006 Concurso Anual de la Cerámica de Mata Ortiz
Mata Ortiz and Casas Grandes

The macaw pens at Paquimé
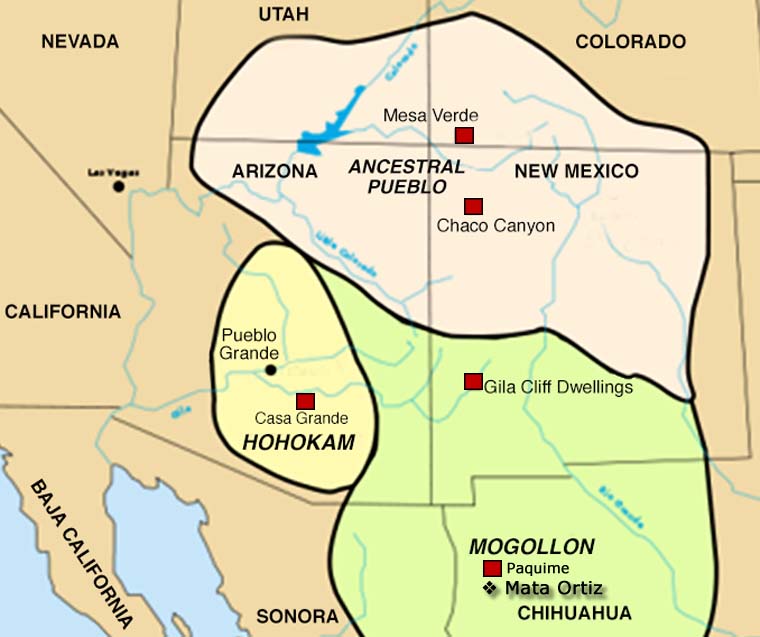
Casas Grandes is both a municipality and an archaeological district in northern Chihuahua State, Mexico. The archaeological district includes the pre-historic ruins of Paquimé, a city that began to build around 1130 AD and was abandoned about 1450 AD. Archaeologists are uncertain as to whether Paquimé was settled by migrants from the Mogollon/Mimbres settlements to the north or by Anasazi elite from the Four Corners region in the United States or by others. Over the years Paquimé was built into a massive complex with structures up to six and seven stories high with multiple Great Houses in the surrounding countryside. Today, the site is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Mata Ortiz is a small settlement inside the bounds of the Casas Grandes municipality very near the site of Paquimé. The fortunes of the town have gone up and down over the years with a real economic slump happening after the local railroad repair yard was relocated to Nuevo Casas Grandes in the early 1960's. The town was in steady decline until Juan Quezada, a poor farmer who gathered firewood in the area of the archaeological site, was inspired by fragments of ancient Paquimé pottery and even older fragments of Mimbres forms with bold black-on-white designs littering the ground to learn more.

Ramos Polychrome effigy pot from Paquimé
Quezada was successful in his quest to learn to recreate the ancient process using slightly more modern techniques (although no one in the present tradition uses a potter's wheel). He learned to use sand and other coarse materials for temper. He discovered that dried cow dung made an excellent and inexpensive firing fuel. Instead of using gourds for smoothing he substituted broken hacksaw blades. Instead of using yucca fiber brushes for painting he learned to make brushes with human hair. He persevered in his efforts and by 1971 had produced a kind of polychrome pottery. Since then, most pottery-making in the area has used innovations in the design and decoration of the pots but the materials and the basic crafting of the process have remained the same.
By the mid-1970s, Quezada had attracted a significant number of traders and his work was becoming a commercial success. That is when he began teaching his techniques to his immediate family. They in turn taught other family members, friends and the younger generations. Both women and men were included from the beginning.
Originally called Casas Grandes pottery in the early years of its production, the potters of this tiny village have made such an impact on the pottery communities, including many awards and special recognition from the Presidents of Mexico, that Mata Ortiz pottery is now becoming known around the world.
Today, pottery production has changed the village in many ways as there is now electricity, plumbing, vehicles and more for the residents. Virtually everyone in the small town (2010 population: 1,182) makes their living by working in some part of the pottery-making process, from potters to clay-gatherers to firewood collectors to traders.
Mata Ortiz pottery incorporates elements of contemporary and prehistoric design and decoration, and each potter or pottery family produces their own distinctive, individualized ware. Young potters from surrounding areas have been attracted to the Mata Ortiz revival and new potting families have developed while the art movement continues to expand. Without the restraints of traditional religious practices or gender constraints, a vibrant flow of new ideas has enabled the pottery of Mata Ortiz to avoid the derivative repetition common to virtually all folk art movements. This blend of economic need, gender equality, cultural expression and artistic freedom has produced a unique artistic movement in today's community.
Lower photo is courtesy of David Monniaux, Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported License
Copyright © 1998-2024 by




